Finance and Banking
AI-powered Financial Risk Management: A Streamlined Approach
Inefficiencies in Traditional Risk Management Approaches
Effective risk management is paramount in the dynamic landscape of finance and banking. Identifying and mitigating risks associated with financial transactions, market fluctuations, regulatory compliance, and cybersecurity threats pose significant challenges. The traditional risk management methods often involve manual processes and siloed data, leading to inefficiencies and increased exposure to potential risks. ZBrain provides effective solutions by simplifying processes for risk assessment and decision-making.
I. How ZBrain Enhances Risk Management
ZBrain leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques to transform risk management in the finance and banking sectors. The following comparison illustrates the time and efficiency improvements gained by using ZBrain in various risk management tasks:
| Steps | Without ZBrain Flow | Time Without ZBrain Flow | With ZBrain Flow |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Aggregation | Manual | ~6 hours | Automated by ZBrain Flow |
| Data Cleaning and Preprocessing | Manual | ~10 hours | Automated by ZBrain Flow |
| Query Execution and Data Analysis | Manual | ~8 hours | Automated by ZBrain Flow |
| Report Generation | Manual | ~7 hours | Automated by ZBrain Flow |
| Report Review and Finalization | Manual | ~3 hours | Automated by ZBrain Flow |
| Total | ~34 hours | ~5 hours |
The table above illustrates that ZBrain notably cuts down the time allocated to risk management tasks, reducing it from about 34 hours to approximately 5 hours, yielding significant time and cost efficiencies.
II. Essential Data Inputs
To ensure optimal functionality, ZBrain depends on the following data sources:
| Information Source | Description | Recency |
|---|---|---|
| Market Data Feeds | Real-time market prices, indices, and economic indicators | Continuous, real-time |
| Internal Transaction Data | Historical transaction records, customer profiles, and trading patterns | Always updated |
| Regulatory Compliance Database | Information on compliance with regulatory requirements and legal obligations | Continuous monitoring |
| News and Social Media Feeds | Real-time news and social media sentiment analysis related to financial markets | Continuous, real-time |
| Credit Ratings and Financial Statements | Credit reports, financial health assessments, and publicly available financial statements | Last fiscal year |
| Internal Documents | Operational manuals, IT security policies, compliance documents, and incident reports | Always updated |
| Industry Reports and Publications | Documentations, published materials, and optimal methodologies | Continuous updates |
| Historical Data on Operational Incidents | Data on IT failures, human errors, compliance issues, cybersecurity incidents, and vendor disruptions | Always updated |
III. ZBrain Flow: How It Works?

Step 1: Data Acquisition and Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
In its initial phase, ZBrain automatically collects relevant data from diverse sources, such as real-time market prices, internal transaction records, regulatory compliance databases, news and social media feeds, credit ratings, and financial statements. Subsequently, ZBrain begins an automatic EDA to reveal insights, comprehend data structure and identify missing values, connections, and patterns that influence risk assessment in the finance and banking sector.
Step 2: Embedding Generation
During this phase, ZBrain converts textual data into numerical representations through sophisticated embedding techniques such as word embeddings or sentence embeddings. These embeddings capture semantic meanings and relationships among data points, enabling efficient data retrieval and analysis. This numerical transformation empowers ZBrain to provide precise insights, enhancing decision-making processes for financial institutions.
Step 3: Query Execution and Report Generation
Whenever a user submits a risk management analysis report query, ZBrain fetches relevant data based on the query requirements. This fetched data and the query are then passed to the Open AI Large Language Model(LLM) for report generation.
The LLM understands and contextualizes the data using the acquired embeddings, deeply exploring the information provided. Leveraging information from the dataset, query particulars, and the intended structure of the report, the LLM dynamically produces a thorough and cohesive report for risk management analysis.
Step 4: Parsing the Generated Report
Once the risk management analysis report is generated in text format, a meticulous parsing process is initiated, expertly extracting essential information like identified risks, potential impacts on business operations, recommended mitigation strategies, and conclusions. This parsed data is then thoughtfully structured, ensuring the final report adheres precisely to the desired format, sections, and report guidelines.
Enhanced Risk Mitigation and Decision-making
ZBrain significantly impacts risk management in the finance and banking industry by automating time-consuming tasks and improving the overall efficiency of risk assessment processes. The substantial reduction in time spent on manual risk mitigation approaches, from approximately 34 hours to just around 5 hours, allows financial institutions to respond promptly to emerging risks, make informed decisions, and implement effective mitigation strategies. Embrace the power of ZBrain to elevate risk management practices and safeguard the stability and success of financial operations.
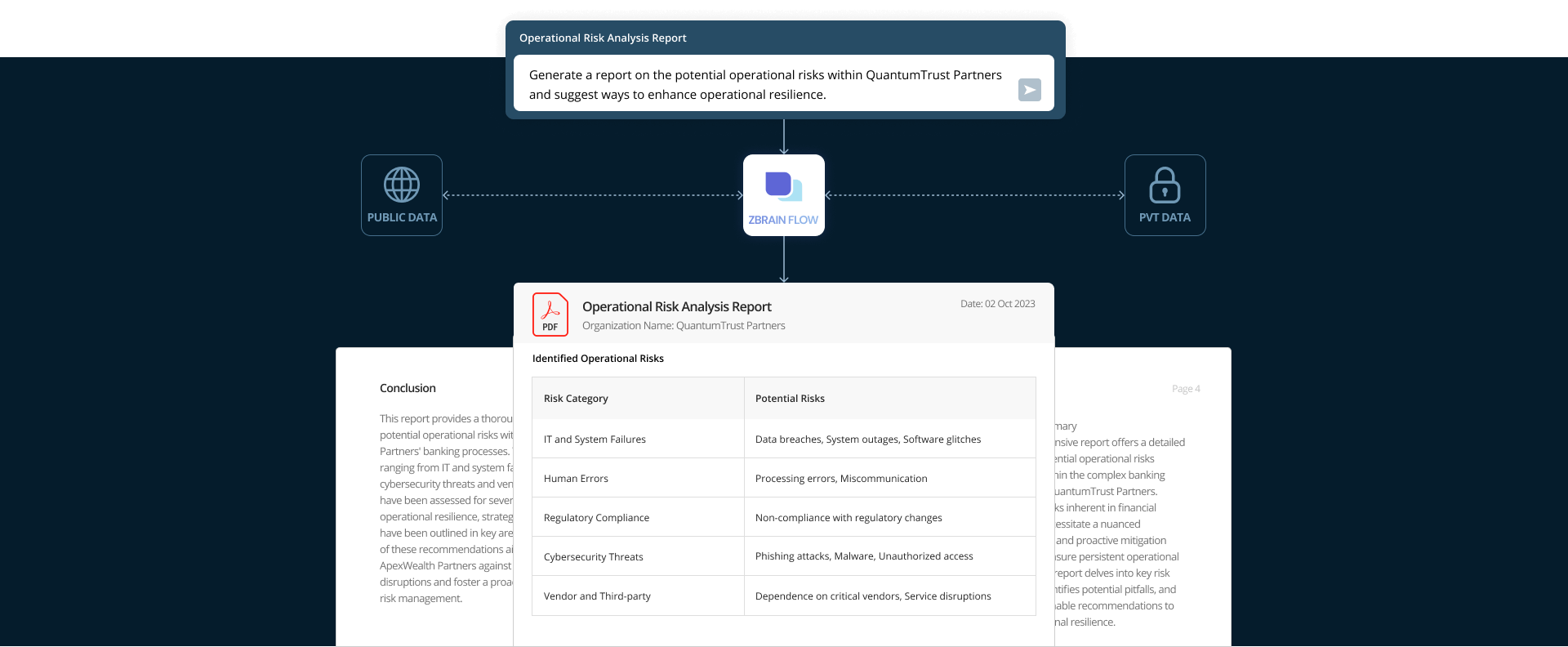
Prompt:
Generate a report on the potential operational risks within QuantumTrust Partners and suggest ways to enhance operational resilience.

Executive Summary
This comprehensive report offers a detailed analysis of potential operational risks embedded within the complex banking processes of QuantumTrust Partners. Operational risks inherent in financial institutions necessitate a nuanced understanding and proactive mitigation strategies to ensure persistent operational resilience. The report delves into key risk categories, identifies potential pitfalls, and provides actionable recommendations to fortify operational resilience.
Overview of Operational Risks
Operational risks within banking processes can stem from diverse factors, including system failures, human errors, regulatory changes, and cyber threats. Understanding this risk landscape is imperative for effective and proactive risk management.
Methodology
The comprehensive analysis presented in this report follows a structured methodology designed to identify, assess, and provide actionable recommendations to mitigate operational risks. The methodology encompasses the following key steps:
-
Risk Identification:
Reviewed internal documents such as operational manuals, IT security policies, compliance documents, and incident reports to gather data on historical operational incidents, existing risk mitigation measures, and regulatory compliance efforts. -
Industry Research:
Leveraged industry reports, publications, and best practices in the banking and financial sector to identify common operational risks similar institutions face. This provided a broader context for assessing QuantumTrust Partners’ risk landscape. -
Regulatory Analysis:
Examined relevant financial regulations and compliance requirements applicable to QuantumTrust Partners. This included thoroughly reviewing recent regulatory changes and their potential impact on the organization’s operational processes. -
Incident Data:
Analyzed historical data on operational incidents within QuantumTrust Partners, including IT system failures, human errors, compliance issues, cybersecurity incidents, and disruptions related to vendors or third-party services. -
Risk Severity Assessment:
Analyzed internal reports to assess the potential severity and impact of identified risks on QuantumTrust Partners. The severity ratings were assigned based on a scale of 1 to 5, considering both the likelihood and consequences of each risk.
Identified Operational Risks
QuantumTrust Partners operates in a dynamic financial landscape where the convergence of technology, human interactions, regulatory requirements, and external partnerships forms the foundation of its banking processes. In this intricate environment, the organization faces several operational risks that could disrupt its functioning and compromise the integrity of its services. The identified operational risks can be broadly categorized into five key areas:
| Risk Category | Potential Risks |
|---|---|
| IT and System Failures | Data breaches, system outages, software glitches |
| Human Errors | Processing errors, miscommunication |
| Regulatory Compliance | Non-compliance with regulatory changes |
| Cybersecurity Threats | Phishing attacks, malware, unauthorized access |
| Vendor and Third-Party | Dependence on critical vendors, service disruptions |
Risk Severity Assessment
Each identified risk undergoes a meticulous assessment for its potential severity and impact on QuantumTrust Partners, rated on a scale of 1 to 5, with 5 indicating the highest severity.
| Risk Category | Severity Rating |
|---|---|
| IT and System Failures | 2 |
| Human Errors | 3 |
| Regulatory Compliance | 2 |
| Cybersecurity Threats | 4 |
| Vendor and Third-Party | 3 |
Key Recommendations for Enhanced Operational Resilience
To fortify operational resilience, consider the following recommendations across various domains:
- IT and System Failures
-
Conduct regular and rigorous system audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities.
-
Establish a robust backup and recovery system for critical data.
-
Provide continuous and targeted training to staff on IT security best practices.
- Human Errors
-
Strengthen communication protocols and provide additional training on meticulous documentation.
-
Implement dual verification processes for critical transactions.
-
Foster a culture of continuous improvement and learning through ongoing training programs.
- Regulatory Compliance
-
Regularly monitor and proactively update compliance policies based on evolving regulatory changes.
-
Conduct periodic compliance audits to ensure unwavering adherence.
-
Establish a dedicated compliance team to stay abreast of regulatory developments and swiftly implement necessary adjustments.
- Cybersecurity Threats
-
Implement advanced and adaptive cybersecurity measures, including the integration of multi-factor authentication.
-
Conduct regular cybersecurity awareness training for all employees.
-
Collaborate with cybersecurity experts to leverage threat intelligence and fortify the institution’s cyber defenses.
- Vendor and Third-party
-
Diversify critical vendors to minimize dependency risks and enhance resilience.
-
Implement stringent vendor risk management protocols, including regular assessments and monitoring.
-
Develop robust contingency plans to address and mitigate service disruptions from key vendors swiftly.
Conclusion
This report provides a thorough examination of potential operational risks within QuantumTrust Partners’ banking processes. The identified risks, ranging from IT and system failures to cybersecurity threats and vendor dependencies, have been assessed for severity. To enhance operational resilience, strategic recommendations have been outlined in key areas. Implementation of these recommendations aims to strengthen QuantumTrust Partners against potential disruptions and foster a proactive approach to risk management.




